AI Tips & Prompts for Educators: Enhancing Student Engagement

In today’s higher education environment, students are not just learners—they are digital natives who expect interactive, personalized, and dynamic learning experiences. Traditional lectures are no longer enough to sustain student attention or encourage deep critical thinking. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes a transformative tool for college and university educators.
AI-powered teaching strategies can help professors simplify lesson planning, enhance student engagement, personalize feedback, encourage research-oriented learning, and create more inclusive classroom environments. The key is using AI strategically and ethically, not as a replacement for teaching, but as a collaborative enhancement tool.
This comprehensive guide provides practical AI tips, classroom-tested strategies, ready-to-use AI prompts, activity ideas, and academic integrity safeguards. You will learn how to use AI to increase student motivation, improve participation, and inspire meaningful learning outcomes.
1. Understanding Student Engagement in Higher Education

Student engagement in universities is shaped by multiple factors: relevance of course material, teaching style, classroom environment, and emotional connection to the subject. Unfortunately, many students struggle with:
- Lecture fatigue
- Information overload
- Limited personalized guidance
- Lack of intrinsic motivation
- Passive note-taking instead of active learning
According to a 2022 Gallup survey, only 32% of college students feel actively engaged in their classes. This means nearly two-thirds are mentally disengaged, even while physically present.
What Students Expect Today
Modern students value:
- Interactive discussions
- Personalized learning pathways
- Real-world application
- Flexibility in learning formats
- Digital integration in coursework
AI enables precisely these enhancements—when used with strategy and pedagogy in mind.
2. The Role of AI in Enhancing Learning Experiences
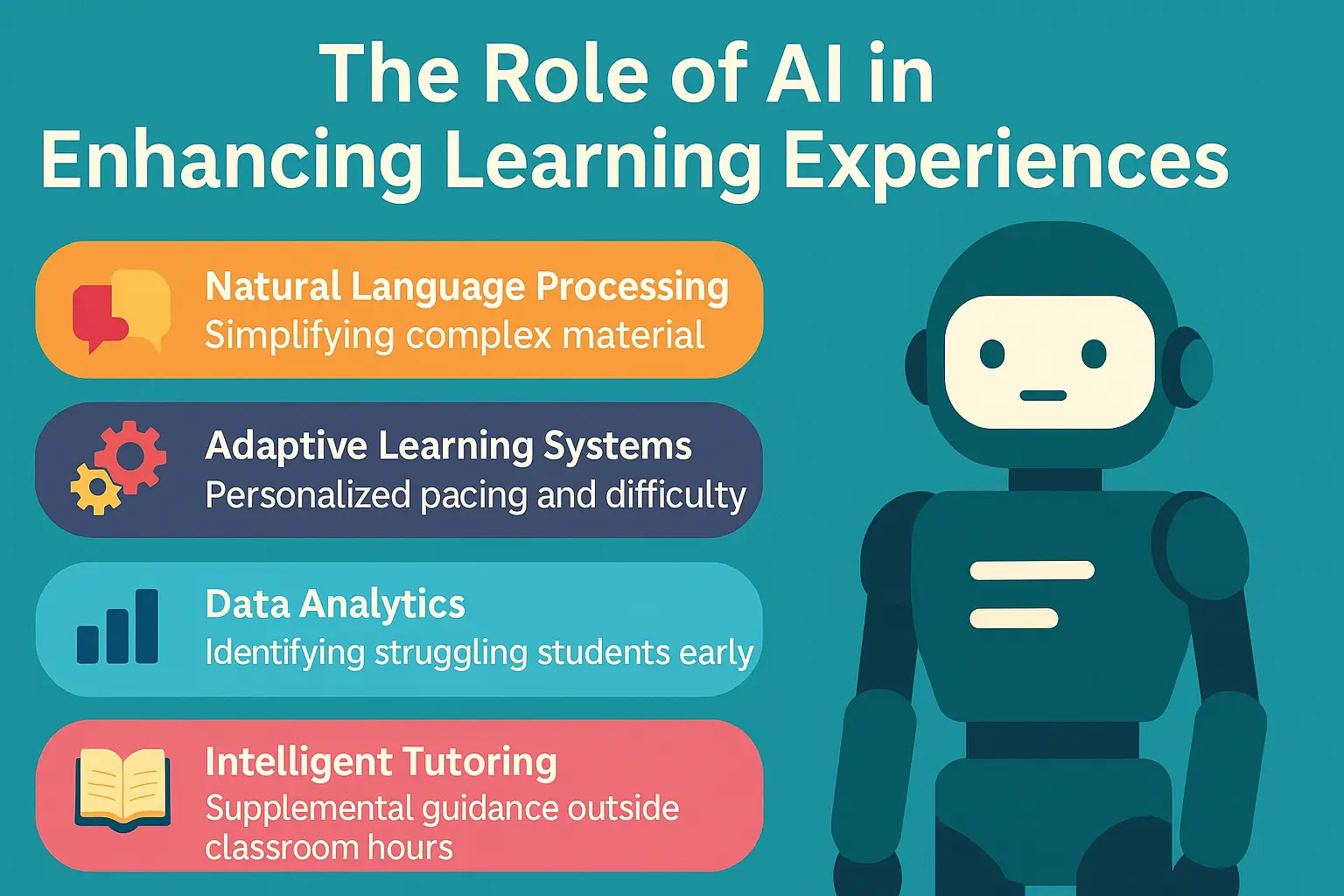
AI is not just ChatGPT or generative text. It encompasses:
| AI Capability | Educational Application |
|---|---|
| Natural Language Processing | Simplifying complex material, academic writing help |
| Adaptive Learning Systems | Personalized pacing and difficulty |
| Data Analytics | Identifying struggling students early |
| Intelligent Tutoring | Supplemental guidance outside classroom hours |
Benefits for University Professors
- Reduce time spent on repetitive tasks
- Create personalized learning opportunities
- Improve clarity and quality of teaching materials
- Foster higher-order thinking and academic discussion
- Increase student participation through interactive prompts
AI does not replace you.
It frees time so you can focus on guiding, mentoring, and challenging students intellectually.
3. Best AI Tools for College Professors
| Tool Name | Primary Use | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT / GPT-5 | Lesson planning, examples, prompting discussions | Best when prompts are specific |
| Google Gemini | Summaries, visual explanations | Strong at logic reasoning |
| Perplexity.ai | Research assistance with citations | Excellent for academic referencing |
| Notion AI | Content organization and syllabus creation | Great for course planning |
| QuillBot / Grammarly | Academic tone editing | Supports student thesis work |
| EdPuzzle | Interactive video lessons | Engaging for flipped classrooms |
| Khanmigo (by Khan Academy) | AI Tutor | Safe for student learning support |
When integrating tools, always disclose usage ethically and encourage responsible academic practices.
4. AI Classroom Prompts to Improve Engagement
AI prompts are instructions you give to an AI model to generate meaningful responses. For education, prompts must encourage analysis, synthesis, evaluation, and reflection (Bloom's Taxonomy).
Discussion Starter Prompts
Use these to spark classroom debates:
- “Explain [topic] in the style of a debate between two scholars with opposing viewpoints.”
- “Generate real-world scenarios where this theory applies incorrectly or has limitations.”
Critical Thinking Prompts
Encourage deeper inquiry:
- “What assumptions does this argument rely upon? Are they justified?”
- “Rewrite this research finding for a non-expert audience without losing accuracy.”
Lecture Enhancement Prompts
For better lesson clarity:
- “Summarize this complex topic into three key ideas suitable for second-year undergraduates.”
- “Create a visual explanation metaphor for understanding this process.”
Student Assignment Prompts
Give direction but maintain academic integrity:
- “Generate structured research questions on this topic, but do not provide answers.”
This ensures students think, not copy.
5. AI-Powered Assessment & Feedback Techniques
AI can reduce grading workload while improving feedback quality.
Use AI to:
- Create rubrics tailored to learning outcomes
- Provide formative (not final-answer) feedback
- Highlight unclear arguments in student writing
- Suggest improvements in academic tone and structure
Example Professor Prompt:
“Evaluate this essay based on clarity, coherence, evidence usage, and academic tone. Provide suggestions but do not rewrite the student’s work.”
Caution:
Do not outsource final grading to AI.
AI assists judgment; it does not replace academic assessment integrity.
6. Encouraging Critical Thinking in the Age of AI
One concern among educators is that AI might limit student originality. However, research from Stanford University (2023) shows that AI can enhance critical thinking when used as a "thinking partner" rather than a solution generator.
Strategies:
- Require students to compare AI-generated responses with peer-reviewed sources
- Ask students to critique AI’s errors
- Make AI output the starting point, not the end product
The goal is to teach students how to evaluate knowledge, not just consume it.
7. Ethical Use of AI in Academic Settings
Students must be taught to cite AI usage, just like books or journals.
Classroom Integrity Guidelines:
- Clarify when AI assistance is allowed
- Require reflection papers on how AI influenced their thinking
- Use plagiarism + AI detection tools ethically (Turnitin AI checker, GPTZero)
- Promote transparent and accountable research practices
AI policy should be part of your syllabus.
8. Real Examples from University Classrooms
| University | Subject Area | AI Use Case | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| University of Michigan | Engineering | AI-generated problem variations | Reduced cheating, increased practice |
| University of Toronto | Literature | AI used as a “text critic” | Improved analytical reading |
| IIM Bangalore | MBA | AI scenario-based case studies | Increased participation in discussions |
These examples show that AI enriches learning when intentionally integrated.
9. Step-by-Step Implementation Framework
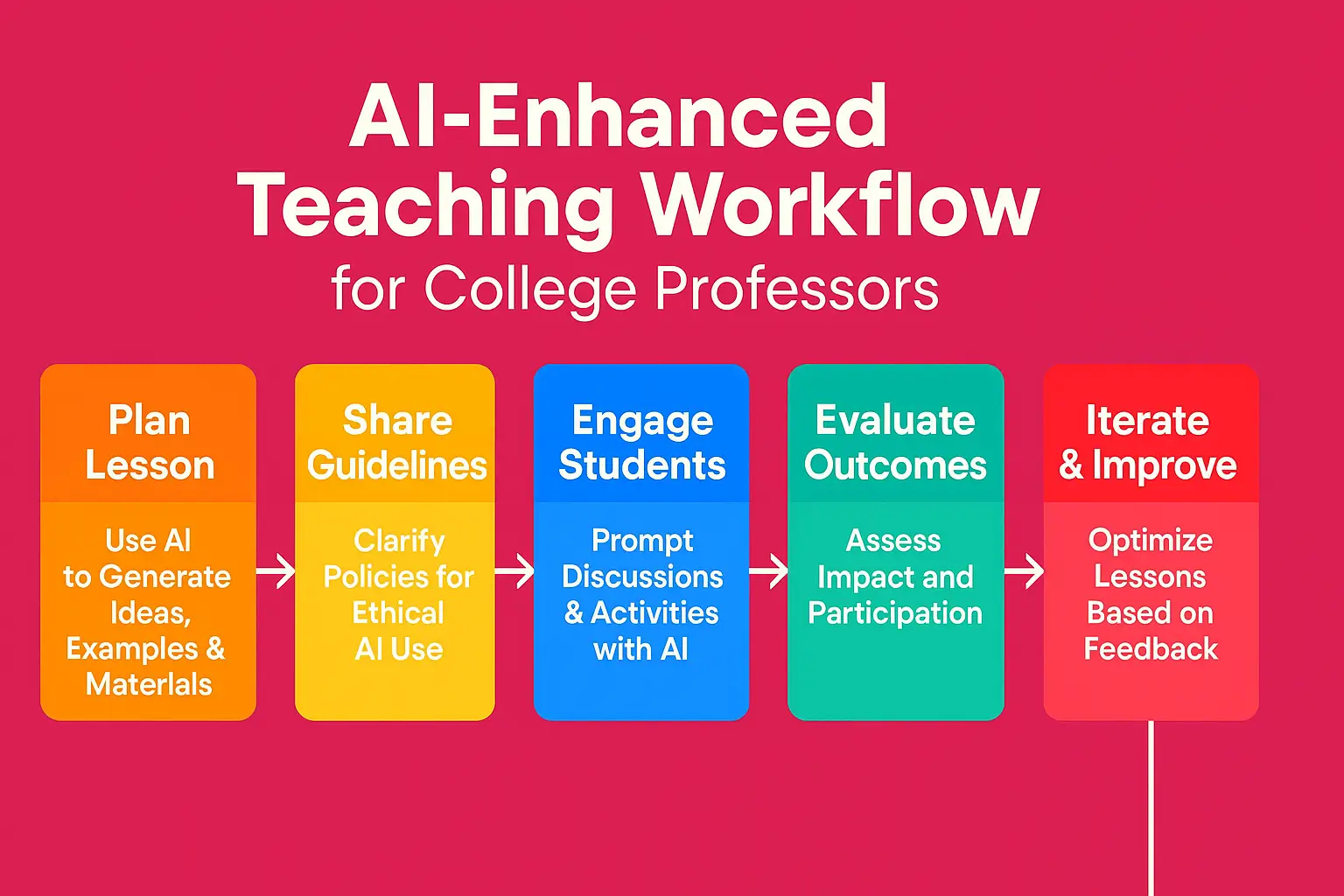
- Start with one AI-assisted lesson per week
- Share ethical usage guidelines
- Encourage group-based AI collaboration
- Use AI to create discussion prompts, not answers
- Evaluate outcomes and adjust accordingly
Over time, AI becomes a natural teaching enhancement, not a disruption.
10. Conclusion & Action Plan
AI is reshaping education—but professors remain the intellectual center of the learning experience.
To enhance student engagement:
- Use AI to simplify instruction, not replace thinking
- Apply prompts that require reasoning and reflection
- Encourage students to analyze rather than copy
- Maintain ethical transparency and academic rigor
The future of higher education belongs to educators who embrace AI thoughtfully and strategically.
11. FAQs
Q1: Can AI replace university professors?
No. AI supports instruction, but learning requires mentorship, critical guidance, and human interaction.
Q2: How do I prevent students from cheating with AI?
Guide them toward reflective assignments and require AI usage transparency.
Q3: Are AI tools safe for all disciplines?
Yes, although STEM, humanities, and applied sciences require different prompt strategies.
Q4: Should AI feedback be used in grading?
It may inform judgment, but human evaluation must remain primary.
Q5: How do I introduce AI to students unfamiliar with it?
Start with low-risk activities like brainstorming and summarization.




